[無料ダウンロード! √] p(x y) 242099-P(x y) calculator
Dy / dx P (x) y = Q (x) where P (x) and Q (x) are functions of x If we multiply all terms in the differential equation given above by an unknown function u (x), the equation becomes u (x) dy / dx u (x) P (x) y = u (x) Q (x)Observe that according to Euler's totient formula, let a be any integer coprime to p, then (a, p) = 1 Then a^ (phi (p)) â ¡ 1 (mod p) Now since p is prime, all a in Z/PZ is coprime to p and phi (p) = (p1) Then (xy)^p = (xy) (xy)^ (p1) (mod p) â ¡ (xy) (1) (mod p)It seems that there's tendency to agree upon p (x)⇒∀xp (x) is the same as ∀x (p (x)⇒∀yp (y)), whereas ∀x (p (x)⇒∀yp (y)) is read as if p (x) is true for some x, then it is true for all x However I don't understand where's the quantifier SOME came from, since there no quantifier '∃' in '∀x (p (x)⇒∀yp (y))'

Complete Parts A Through F Below To Find Nonnegative Numbers X And Y That Satisfy The Homeworklib
P(x y) calculator
P(x y) calculator-Sometimes it really is, but in general it is not Especially, Z is distributed uniformly on (1,1) and independent of the ratio Y/X, thus, P ( Z ≤ 05 Y/X) = 075 On the other hand, the inequality z ≤ 05 holds on an arc of the circle x 2 y 2 z 2 = 1, y = cx (for any given c) The length of the arc is 2/3 of the length of the circle0 < x < 1;


Http Www Cs Cmu Edu b Slides Nbayes Pdf
P(X= 129) = P(X= 129 and Y = 15) P(X= 129 and Y = 16) = 012 008 = 0 What is the probability distribution of X?Given random variables X, Y, {\displaystyle X,Y,\ldots }, that are defined on a probability space, the joint probability distribution for X, Y, {\displaystyle X,Y,\ldots } is a probability distribution that gives the probability that each of X, Y, {\displaystyle X,Y,\ldots } falls in any particular range or discrete set of values specified for that variable In the case of only two random variables, this is called a bivariate distribution, but the concept generalizes to anyFZ(z) = P(Z ≤ z) = P(X/Y ≤ z) = ˆ 0 if z < 0 P(Y ≥ (1/z)X) if z > 0, where we have used the fact that X and Y are both nonnegative (with probability 1), so multiplying both sides of the inequality by Y does not flip the inequality;
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicP= (X=1/32) because HHHHH is the only answer for 5 heads in a coin toss that occurs five times In this situation, Master Salman is doing a coin toss only three times So there is no probability distribution for 5 heads because that is impossible Thank you!P (X \cap Y) = P (XY) \times P (Y) P (X ∩ Y) = P (X ∣Y) ×P (Y) The probability that A and B occurs is the probability of X occurring, given that Y occurs multiplied by the probability that Y
P Var(X) is called the standard deviation of X For any rv X and any number a E(aX) = aE(X), and Var(aX) = a2Var(X) (3) For any two rvs X and Y E(X Y) = E(X)E(Y) (4) If X and Y are independent, then Var(X Y) = Var(X)Var(Y) (5) The above properties generalize in the obvious fashion to to any finite number of rvs In general (independent or not)Where y i is the vapor mole fraction and y 1 y 2 = 1, x i is the liquid mole fraction and x 1 x 2 = 1 , and P is the total pressure (bar) The bubblepoint pressure is calculated using ΣK i x i = 1Here you graph parabolas using the xintercepts This is one of my favorite, and easier methods, to follow The homework is Pages , #'s 326, and "Qui



Chapter 4 Joint And Conditional Distributions Ppt Download


The Curves X 3 P Xy 2 2 And 3 X 2y Y 3 2 Are Orthogonal For Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
0 < y < x 0;P dilip_k Nov 9, 17 Given that the equation of the chord \displaystyle\ \text{ }\ {\left({x}{y}={2}\ldots{\left{1}\right}\right)} the equation of the circleTrue, then automatically the statement ∀x ∈ A,∃y ∈ B,P(x,y) must be true (but in general it doesn't go the other way) Aside Occasionally, you will see a nested quantifier at the end of a statement, in which case it is implied that the quantifier is the last in terms of order For example, here is the definition of bounded



Complete Parts A Through F Below To Find Nonnegative Numbers X And Y That Satisfy The Homeworklib



A Point P Moves In Xy Plane In Such A Way That X Y 1 Where Denotes The Greatest Integer
X^3 x^2 y x y^2 y^3 Extended Keyboard;What is \(P(X = Y)\), the probability that one samples the same number of red and white balls?If the joint probability density function of random variable X and Y is , (,) , the marginal probability density function of X and Y are = ∫, (,) ,



Pointwise Mutual Information Wikipedia



Se13j01 02 Gif
1 Sum of Independent Binomial RVs • Let X and Y be independent random variables X ~ Bin(n 1, p) and Y ~ Bin(n 2, p) X Y ~ Bin(n 1 n 2, p) • Intuition X has n 1 trials and Y has n 2 trials o Each trial has same "success" probability p Define Z to be n 1 n 2 trials, each with success prob p Z ~ Bin(n 1 n 2, p), and also Z = X Y0 < y < x o (Figure 2) Figure 2 f(x;y)jy < x;0 < x < 1;0 < y < 1g Therefore P (X > Y) = Z 1 0 ˆZ x 0 f(x;y)dy ˙ dx = Z 1 0 ˆZ x 0 6x2ydy ˙ dx = Z 1 0 3x4dx = 3 5 Example 2 Consider random variables X,Y with pdf f(x,y) such that f(x;y) = 8 < 8xy;Let™s calculate P (X > Y) For –xed x o;


Q Tbn And9gcryv25hrg 7 Ojb0cpz3lkqay4lft0yv65wxmj6 Qitsj8jki1h Usqp Cau



Stats Cheat Sheet Coefficient Of Variation Variance
E(X) = (P y E(XY = y)P(Y = y) if Y is discrete, R∞ −∞ E(XY = y)fY (y)dy if Y is continuous You should note that this applies to the probability of an event (which is nothing other than expectation of its indicator) as well — if you know P(AY = y) = E(IAY = y) then you may compute P(A) = EIA by the Bayes formula above Example 111• Probabilities Probabilities involving X and Y (eg, P(X Y = 3) or P(X ≥ Y) can be computed by adding up the corresponding entries in the distribution matrix More formally, for any set R of points in the xyplane, P((X,Y) ∈ R)) = P (x,y)∈R f(x,y) • Expectation of a function ofP X and Y (eg, u(x,y) = xy) E(u(X,Y)) = x,y u(x,y)f(x,y)P dilip_k Nov 9, 17 Given that the equation of the chord \displaystyle\ \text{ }\ {\left({x}{y}={2}\ldots{\left{1}\right}\right)} the equation of the circle


Www Ics Uci Edu Xhx Courses Cs273p 03 Bayesclass 273p Pdf


If The Distances Of P X Y From The Points A 3 6 And B 3 4 Are Equal Prove That 3x Y 5 From Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Punjab Board
There are 421 words containing P, X and Y ANAPHYLAXES ANAPHYLAXIES ANAPHYLAXIS XYLOPYROGRAPHY XYLOTYPOGRAPHIC XYLOTYPOGRAPHY Every word on this site can be played in scrabbleNote, however, that when we divide both sides by z, to obtain Y ≥ (1/z)X, we were making the assumptionP (X \cap Y) = P (XY) \times P (Y) P (X ∩ Y) = P (X ∣Y) ×P (Y) The probability that A and B occurs is the probability of X occurring, given that Y occurs multiplied by the probability that Y


Text Classification


3
Where y i is the vapor mole fraction and y 1 y 2 = 1, x i is the liquid mole fraction and x 1 x 2 = 1 , and P is the total pressure (bar) The bubblepoint pressure is calculated using ΣK i x i = 11 Let u(x, y) = x (3/4) * y (1/4), p x = 5, p y = 3, and I = 60 Now assume that p' x = 9 Separate the income effect and substitution effect using the Slutsky method Show your work on the graph too Compare the value of the point that separates these two effects you found here with the one we found for the Hicksian method in the class 2If the joint probability density function of random variable X and Y is , (,) , the marginal probability density function of X and Y are = ∫, (,) ,


P Xy And T Xy Diagram Equilibrium Thermodynamics



If P X Y Is Any Point On The Line Joining The Points A A 0 And B 0 B Then Show That X A Y B 1 Brainly In
PX(x)=P(X=x)forallx Theprobabilitydistributionforadiscreterandomvariableassignsnonzero probabilities toonly a countable number ofdistinct x values Any value x not explicitly assigned a positive probability is understood tobe such that P(X=x) = 0 The function pX(x)= P(X=x) for each x within the range of X is called the probability distribution of XPX(x)=P(X=x)forallx Theprobabilitydistributionforadiscreterandomvariableassignsnonzero probabilities toonly a countable number ofdistinct x values Any value x not explicitly assigned a positive probability is understood tobe such that P(X=x) = 0 The function pX(x)= P(X=x) for each x within the range of X is called the probability distribution of XF(x) = P(X ≤ x) Continuous distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by integration of the probability density function f(u) of continuous random variable X Discrete distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by summation of the probability mass function P(u) of discrete random variable X
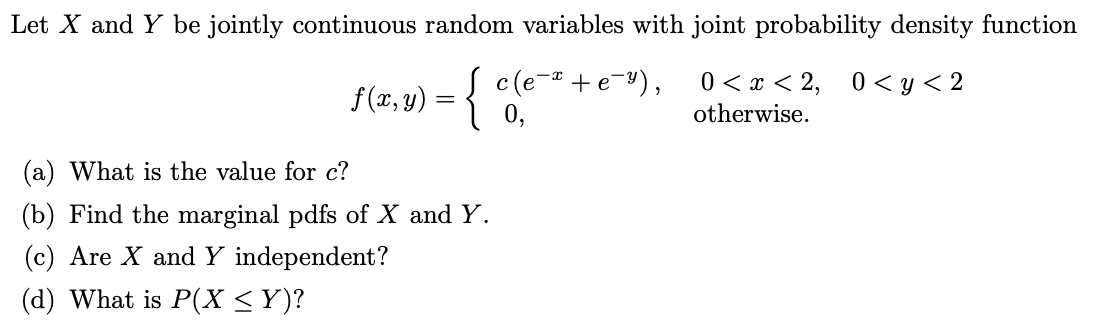


Answered Let X And Y Be Jointly Continuous Bartleby
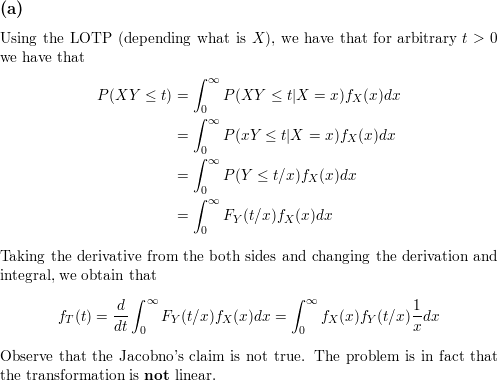


Let X And Y Be Independent Positive R V S With Pdfs Math F X Math And Math F Y Math Respectively And Consider The Product T Xy When Asked To Find The Pdf Of T Jacobno Argues
P(X < 1) = P(X = 0) P(X = 1) = 025 050 = 075 Like a probability distribution, a cumulative probability distribution can be represented by a table or an equation In the table below, the cumulative probability refers to the probability than the random variable X is less than or equal to xWhere y i is the vapor mole fraction and y 1 y 2 = 1, x i is the liquid mole fraction and x 1 x 2 = 1 , and P is the total pressure (bar) The bubblepoint pressure is calculated using ΣK i x i = 1The joint probability mass function of two discrete random variables X and Y is defined as P X Y (x, y) = P (X = x, Y = y) Note that as usual, the comma means "and," so we can write P X Y (x, y) = P (X = x, Y = y) = P ((X = x) and (Y = y))


If The Point P X Y Is Equidistant From The Points A 5 1 And B 1 5 Prove That X Y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Www Cse Unr Edu Bebis Cs479 Ass Ass1sol Pdf
Let P(x,y) be a point on the graph of y=2x5 Express (and simplify) the distance from the origin 0(0,0) to P as a function of x Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our precalculus problem solver and calculatorBy the table, one sees that this is possible only when \(X = 1, Y = 1\) or \(X = 2, Y = 2\) So the probability \ P(X = Y) = f(1, 1) f(2, 2) = \frac{12}{252} \frac{54}{252} = \frac{66}{252}Let the points be P (x,y),A(1,4),B(−1,2)Point P is equidistant from A&BNow, using the distance formulax1 = x, y1 = yx2 = 1, y2 = 4P A= (x2 −x1 )2 (y2 −y1 )2 = (1−x)2 (4−y)2 Similarly for P Bx1 = x, y1 = yx2 = −1, y2 = 2P A= (x2 −x1 )2 (y2 −y1 )2 = (−1−x)2 (2−y)2 we know thatP A= P B(1−x)2 (4−y)2 = (−1−x)2 (2−y)2 Squaring both sides⇒ (1−x)2 (4−y)2 =(−1−x)2 (2−y)2⇒ 1x2 −2x16y2 −8y = 1x2 2x4y2 −4y⇒ −2x−2x−8y4y16−4
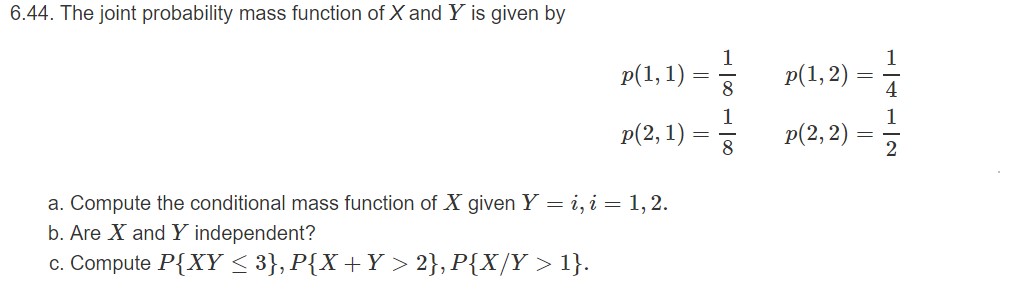


Answered 6 44 The Joint Probability Mass Bartleby
.png)


If A Number X Is Chosen At Random From The Numbers 1 2 3 And The Number Y Is Selected From 1 4 9 Math Probability Meritnation Com
The joint probability mass function of (X;Y) is (12) p(xi;yj) = P(X = xi;Y = yj) Example 1 A fair coin is tossed three times independently let X denote the number of heads on the flrst toss and Y denote the total number of heads Find the joint probability mass function of X and Y 2According to p(x,y) is given by I(X;Y) = X x,y p(x,y)log p(x,y) p(x)p(y) (24) = H(X)−H(XY) = H(Y)−H(YX) = H(X)H(Y)−H(X,Y) (25) 4True, then automatically the statement ∀x ∈ A,∃y ∈ B,P(x,y) must be true (but in general it doesn't go the other way) Aside Occasionally, you will see a nested quantifier at the end of a statement, in which case it is implied that the quantifier is the last in terms of order For example, here is the definition of bounded
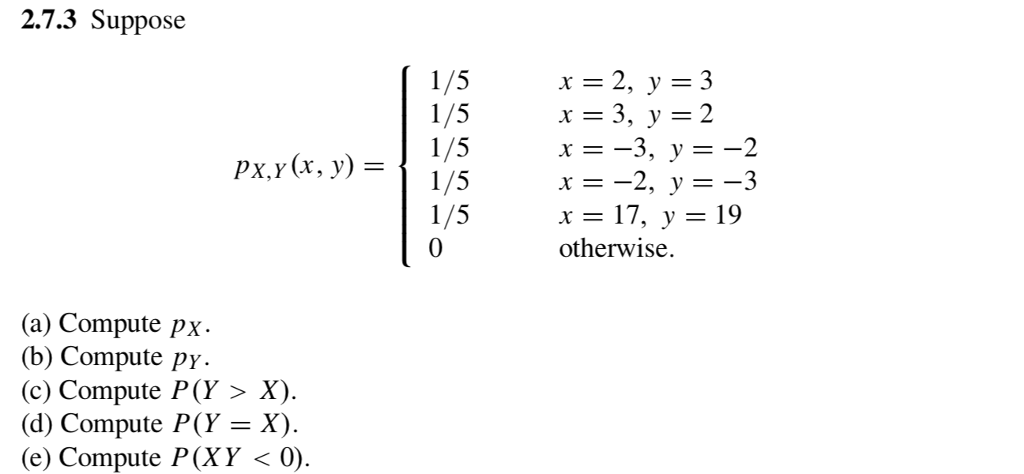


Solved 2 7 3 Suppose 1 5 1 5 1 5 X 3 Y 2 X 3 Y 2 X 2 Chegg Com



2 Let The Random Variables X And Y Have The Joint Pdf Given Below A Find P X Y 2 B Find The Marginal Pdfs O Homeworklib
P(X ≥x) = e−λ(xy) e−λx = e−λy = P(X ≥y), which proves the memoryless property The memoryless property also has a geometric interpretation Consider the probability density function of an exponential(λ) random variable from some value x to infinity The area under the probabilitydensityfunctionfromx toinfinitydoesnotequal1;ratheritequalse−λx Theconditional probability density function given that the random variable X is greater than or equal to x is found by rescaling fP (X) = P (Y) or P (X n Y) = 0 That is, the above is true if and only if X and Y are equally likely, or if X and Y are mutually exclusive Oh, and since we were dividing by P (X) and P (Y), bothExpected Value and Standard Dev Expected Value of a random variable is the mean of its probability distribution If P(X=x1)=p1, P(X=x2)=p2, n P(X=xn)=pn E(X) = x1*p1 x2*p2 xn*pn



A Point P X Y Moves In The Xy Plane Such That X Acos 2theta And Y 2asintheta Where T Youtube


Http Www Eclecticon Info Index Htm Files Probability statistics expectation variance skew kurtosis Pdf
P(X ≥x) = e−λ(xy) e−λx = e−λy = P(X ≥y), which proves the memoryless property The memoryless property also has a geometric interpretation Consider the probability density function of an exponential(λ) random variable from some value x to infinity The area under the probabilitydensityfunctionfromx toinfinitydoesnotequal1;ratheritequalse−λx Theconditional probability density function given that the random variable X is greater than or equal to x is found by rescaling fThe joint probability mass function of two discrete random variables X and Y is defined as P X Y ( x, y) = P ( X = x, Y = y) Note that as usual, the comma means "and," so we can write P X Y ( x, y) = P ( X = x, Y = y) = P ( ( X = x) and ( Y = y)) We can define the joint range for X and Y as R X Y = { ( x, y) P X Y ( x, y) > 0 }X y f x y 1 3 P X x Y y f x y For any region A in the xy plane P X Y A A f x y from MATH MTH02 at Institute of Technical and Education Research



Bayes Theorem Some Perspectives By Garychl Towards Data Science



If The Point P X Y Is Equidistant From A A B B A And B A B A B Prove That Bx Ay Youtube
E(X) = (P y E(XY = y)P(Y = y) if Y is discrete, R∞ −∞ E(XY = y)fY (y)dy if Y is continuous You should note that this applies to the probability of an event (which is nothing other than expectation of its indicator) as well — if you know P(AY = y) = E(IAY = y) then you may compute P(A) = EIA by the Bayes formula above Example 111Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems Get help on the web or with our math appOnline math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems Get help on the web or with our math app


Http Www Cl Cam Ac Uk Teaching 1314 Infotheory Exercises1to4 Pdf


P Xy T Xy Diagrams Equilibrium Thermodynamics
F(x) = P(X ≤ x) Continuous distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by integration of the probability density function f(u) of continuous random variable X Discrete distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by summation of the probability mass function P(u) of discrete random variable XObtain the value P (X − Y > z) we must integrate the joint PDF f X,Y (x, y) over the shaded area in the above figures, which correspond to z ≥ 0 (left side) and z < 0 (right side) For the case z < 0, we can use a similar calculation, but we can also argue using symmetry" ∀ y, ∀ x, P (x, y) " means given any object y, paired with any object x, the statement P is true about them Recall that if A and B are statements, the meaning of


Dtai Cs Kuleuven Be Education Ai Exercises Session8 Solutions Solution Pdf


In Triangle Xyz Angle Xzy 90 Xy Z Units Yz X Units Zx Y Units Zdis Perpendicular To Xy And Zd P Units Prove That 1 P2 1 X2 1 Y2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 7syjn
PX ≤ Y First, let's consider the denominator PX ≤ Y = X z≥1 PX = z ∩z ≤ Y = X z PX = zPz ≤ Y = X z (1−p)z−1p(1−q)z−1 = X z (1−p)(1−q)z−1p = p X z (1−p−q pq)z−1 = p pq −pq The last step above is again by the identity in Eqn 1 Now we can compute the whole equation EXX ≤ Y = pq −pq p X x xPX = xPx ≤ Y = pq −pq p X x



232 Xy P Rayquaza Pokemon Tcg Promo Pokeboon Japan


Sumo Stanford Edu Pdfs Smt19 Algebra Solutions Pdf


Bayes Theorem Solutions Formulas Examples Videos



Find P X Y Le 0 Given The Joint Probability Function Of X And Y Mathematics Stack Exchange



Nanohub Org Resources Me 597uq Lecture 04 Introduction To Probability Theory Ii Watch Presentation



Learning Inequalities Simulating Laplace Random Numbers From Normal Distribution



Tutorial 3 Solution 1 An Instructor Has Given A Short Test Consisting


Q Tbn And9gct1ck8fpzmvcy09br Jwxhbrf6s Byf2nrqxvsl2thghbrtwelt Usqp Cau
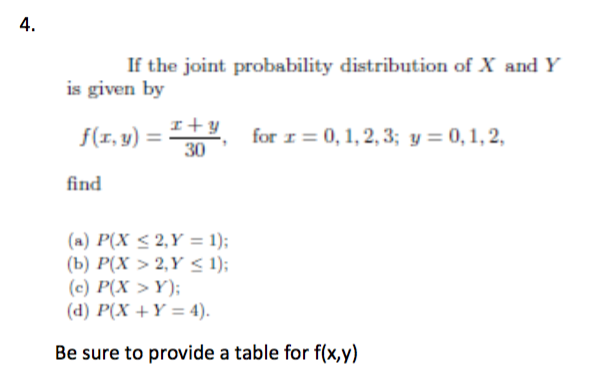


Solved If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y I Chegg Com
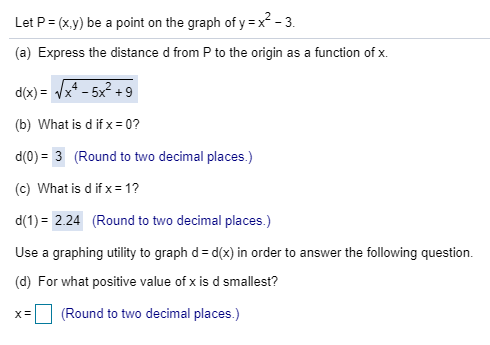


Answered Let P X Y Be A Point On The Graph Of Bartleby



Problems And Solutions 4



7transformation Of Two Random Variables Suppose X Chegg Com



Product Distribution Wikipedia



Integration Bounds With P Xy Z Mathematics Stack Exchange



Processing Math 100 Home Table Of Contents Conditional Distribution Unconditionals In Terms Of Conditionals More Than 2 Variables Substitution Problems For Practice Conditional Distribution Definition Conditional Distribution Let X W S And Y W T Be


Http Www Cs Cmu Edu b Slides Nbayes Pdf



If The Point P X Y Is Equidistant From The Points A 3 6 And B 3 4 Prove That 3x Y 5 0 Brainly In


Www Stt Msu Edu Users Makagon 351 5 1 Pdf



Quiz 2 Soln 1 Pdf Math 217 Quiz 2 Name Soln 1 5 Pts Let P X Y Mean U1cx 2y Xy 00 Where X And Y Are Integers Determine The Truth Value Of The Course Hero


Http Math Arizona Edu Jwatkins Joint Pdf


Random Variable Gate Overflow



Solved Solve The Optimization Problem Hint See Example Chegg Com


Faculty Math Illinois Edu Hildebr 370 370jointdistributions Pdf


Solved 1 1 Pt True False Suppose P X Y Means X 2y Xy X Y Integers 1 2 3 4 5 Determine Truth Value Q2615


If The Point P X Y Is Equidistant From The Points A A B A B And B A B B A Then Prove Bx Ay Studyrankersonline



Let X And Y Have Joint Density Xy 0otherwise 0 Otherwise A Find K B Compute The Homeworklib


Www Utdallas Edu Efrom Solhw Pdf



Average Fp Of P Xy Together With Its Profile With The Periodic Download Scientific Diagram
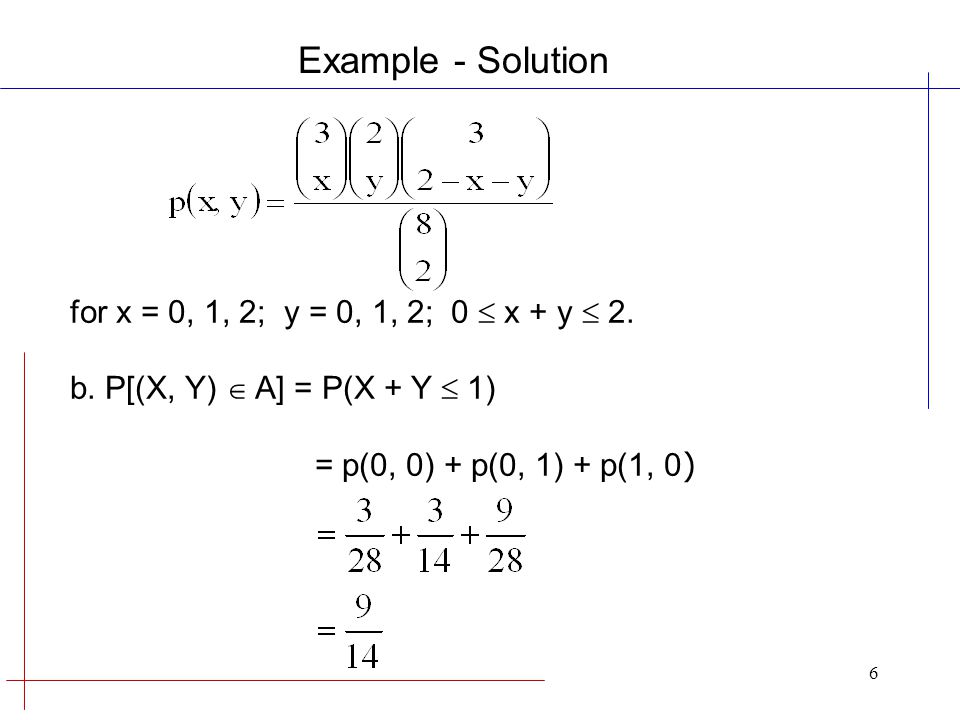


Joint Probability Distributions Leadership In Engineering Ppt Video Online Download


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch3annotated Pdf
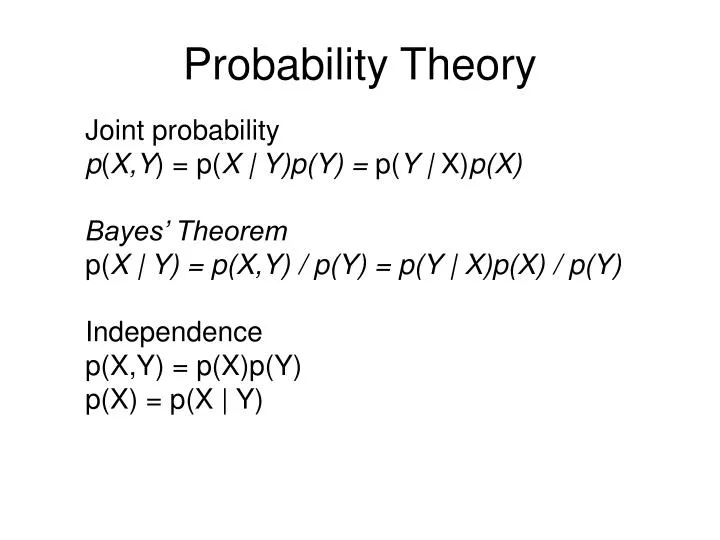


Ppt Probability Theory Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Q 16 Locus Of A Point P X Y Satisfying The Equation Sqrt



What Is Bayes Theorem Applications Of Bayes Theorem
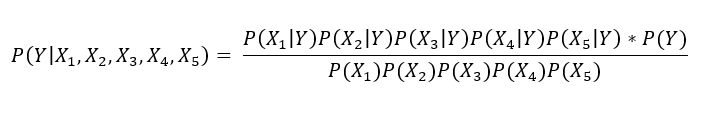


Why Is Naive Bayes Theorem So Naive By Chayan Kathuria The Startup Medium
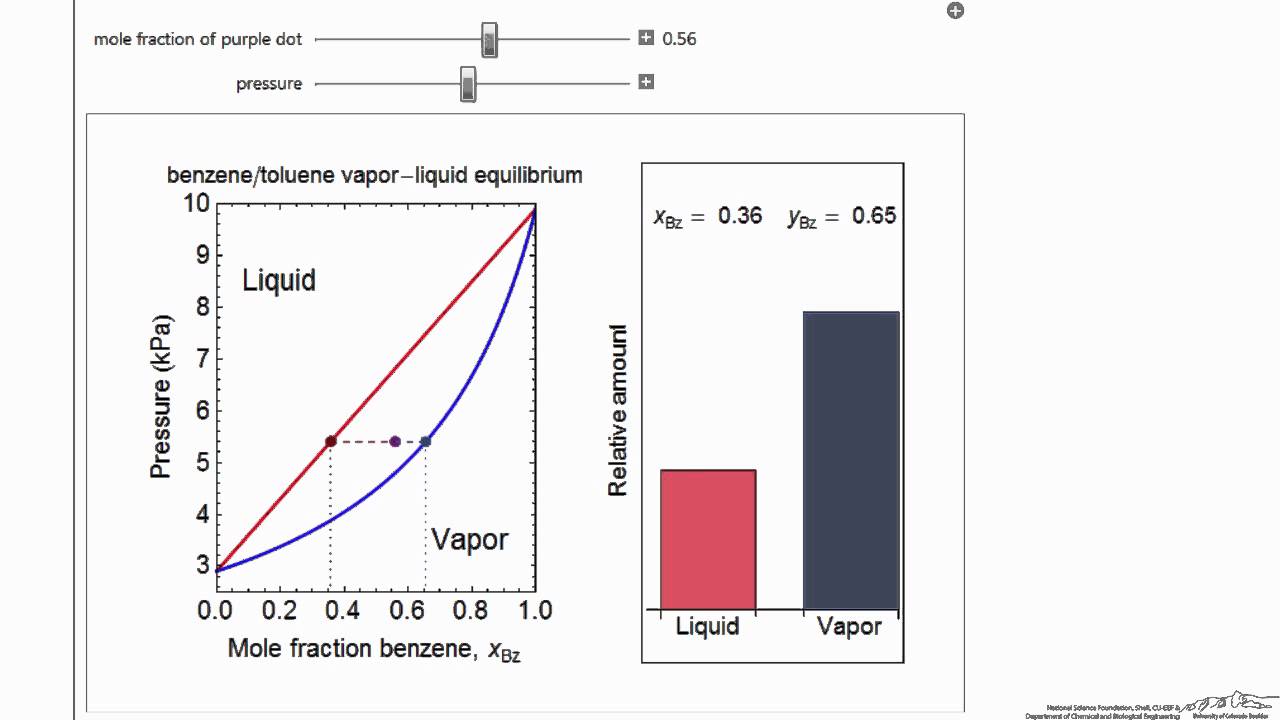


P X Y Diagram For Vle Interactive Simulation Youtube


2



Statistics 100a Homework 7 Solutions Pdf Free Download



Bayesian Efficient Coding Biorxiv
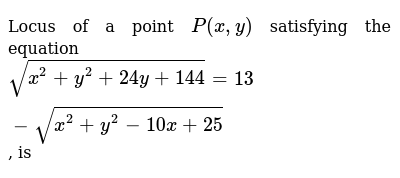


Locus Of A Point P X Y Satisfying The Equation Sqrt X 2 Y



Conditioning Probability Wikipedia



Surfing Pikachu Japanese 264 Xy P Pokemon Trollandtoad



Questions And Answers Cbse Icse Solutions Cbse Icse Study Materials Online Learning Question Papers Classnotes Practice Test Mcq



Find The Distance Between A Point P Xy From Orgin Brainly In



Solved Let The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y Chegg Com
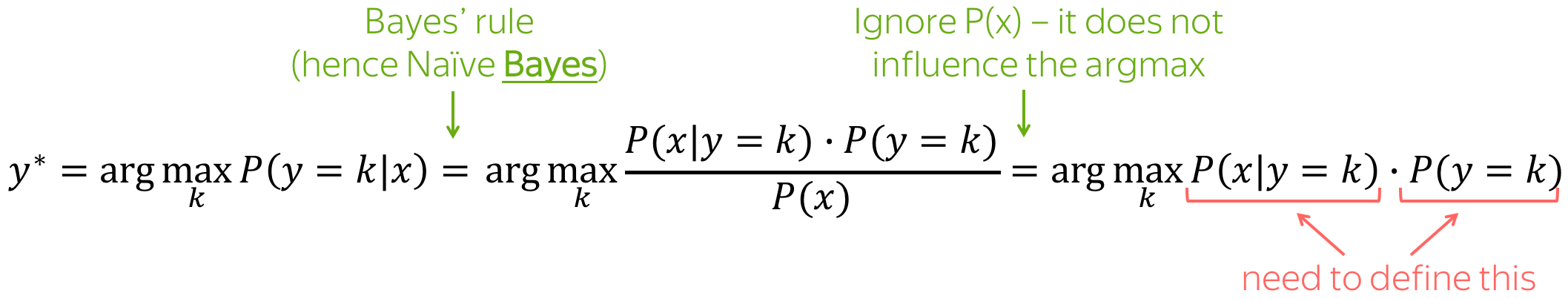


Text Classification


Q Tbn And9gcrwhzokremzetz Tgkypcv94zovgjvr2lzwuhvm Vzrww1fto Usqp Cau


A Primer On Learning In Bayesian Networks For Computational Biology



Let X And Y Be Two Events Such That P X 1 3 P X Y 1 2and P Y X



P 6 2 P 629 2 Pihera Xy Piezo Stage



Why Is Displaystyle Sum Y P X X Y Y P X X Mathematics Stack Exchange


2
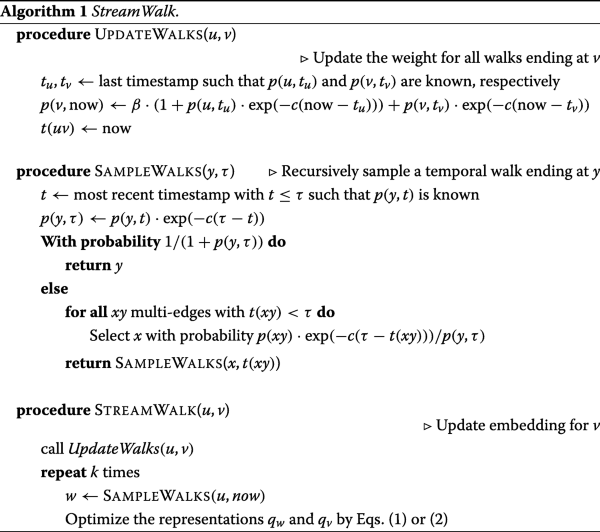


Node Embeddings In Dynamic Graphs Applied Network Science Full Text



Total Expectation Theorem



Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download



A Generative Approach To Classification By Rahul Agarwal Towards Data Science
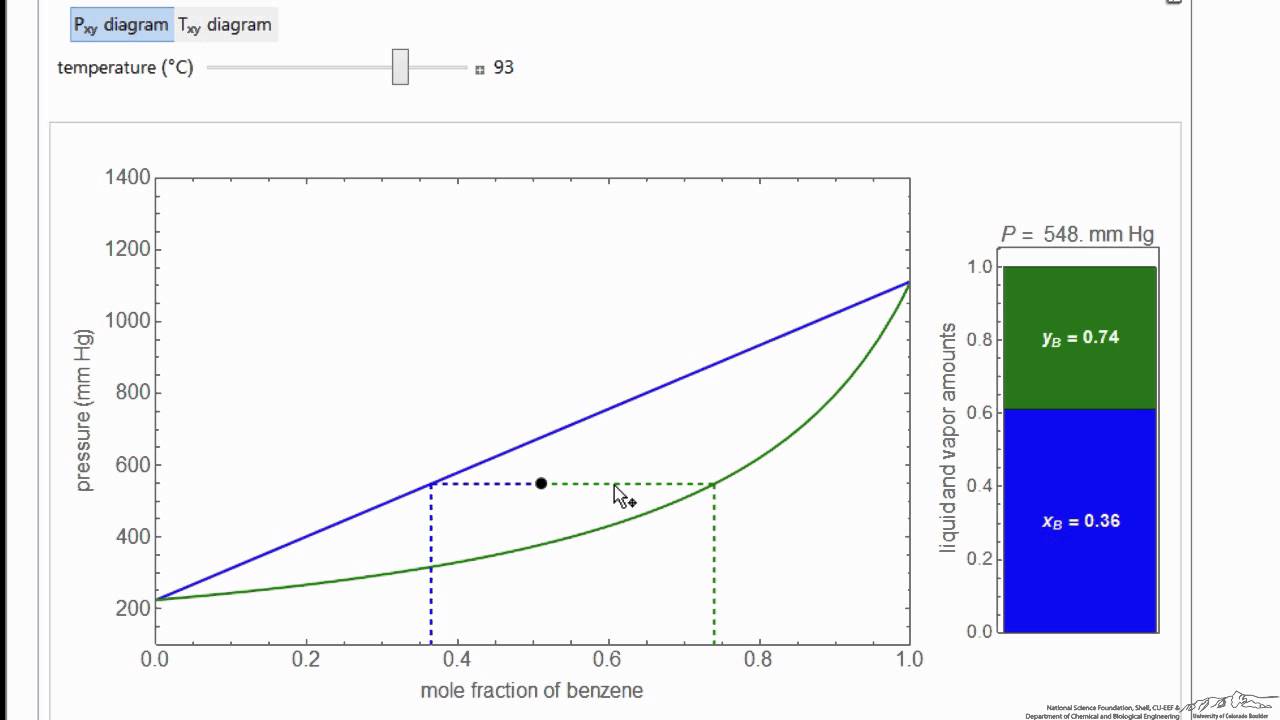


P Xy And T Xy Diagram Equilibrium Thermodynamics



Newbold Chapter 4 Part2 Stat 210 0 Studocu



66 For What Values Of P Y 2 X Y P X



Poison Distribution Homework Help



Gibbs Distribution


Canvas Harvard Edu Courses 376 Files 243 Download Verifier Y5ddnrzr3zaacau4gue7qt8g3o4zmiqey5oefscx



Example 14 Check True Or False By Proving Its Contrapositive
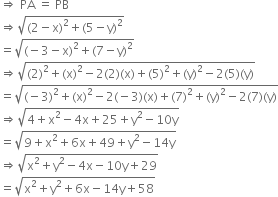


Find A Relation Between X And Y Such Thai The Point P X Y Is Equidistant From The Points A 2 5 And B 3 7 From Mathematics Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Uttarakhand Board


If The Distances P X Y From A 5 1 And B 1 5 Are Equal Then Prove That 3x 2y Mathematics Topperlearning Com


Http Www Math Wisc Edu Boston 729newhw4 Pdf



Q7 Find X Y And P Is The Given Figures Lido
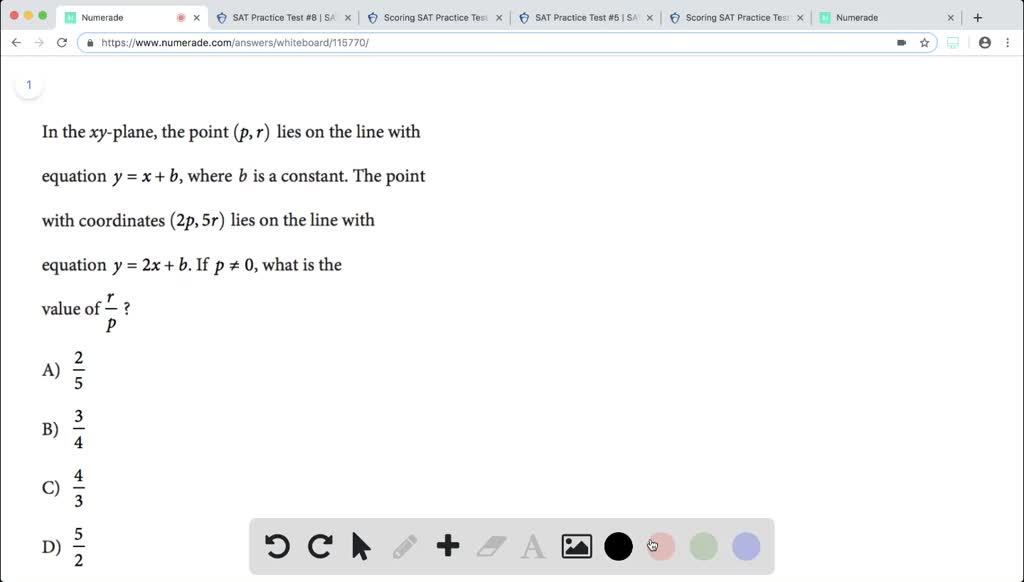


Solved In The X Y Plane The Point P R Lies O



Optimization Problems


Joint Probability Distributions


Http Www Math Uiuc Edu Rsong 461f10 Whw10s Pdf


Continuous Random Variables Media Hopper Create
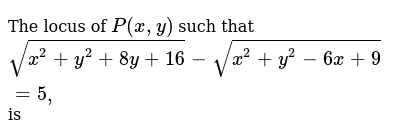


The Locus Of P X Y Such That Sqrt X 2 Y 2 8y 16 Sqrt X 2 Y 2



How To Find The Mean And Variance Of Minimum Of Two Dependent Random Variables


The Pillars Curriculum For Chemical Engineering


コメント
コメントを投稿